




Hydraulic Guillotine Shearing Machine
Key words:
Hydraulic Guillotine Shearing Machine
Classification:
- Product Description
- Components
- Technical Parameters
-
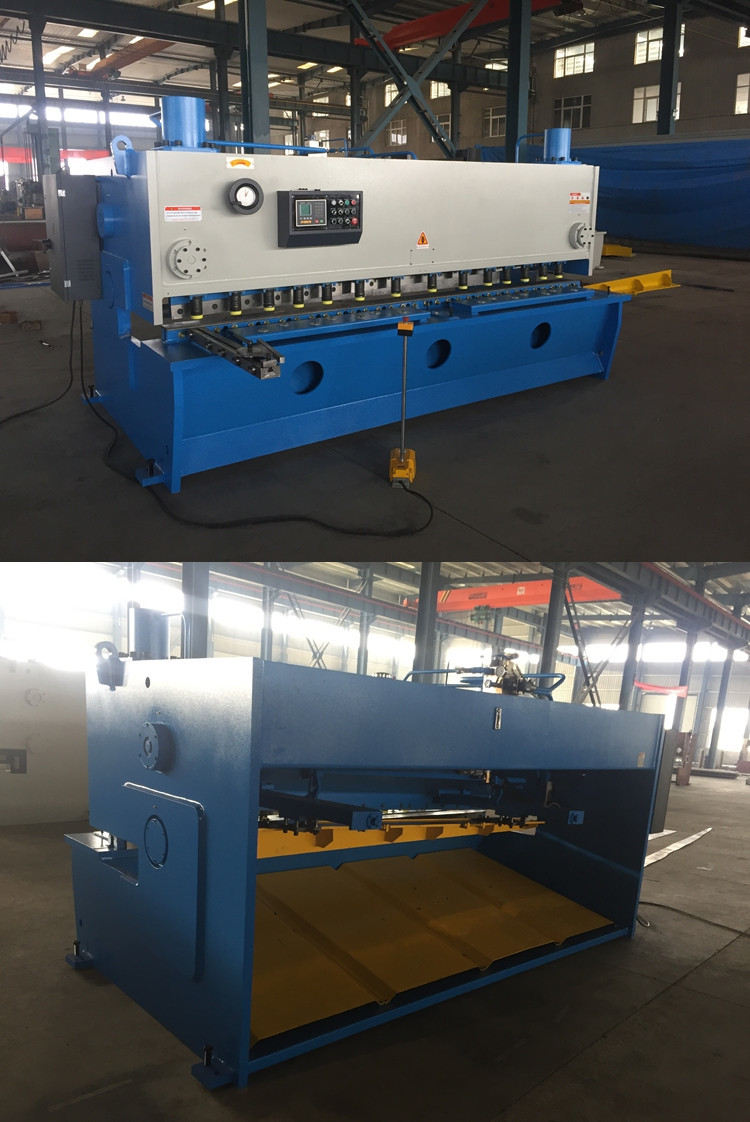
QC11K Hydraulic guillotine shearing machine
Features:
Steel-welded machine body with vibration stress relief, excellent rigidity and stability.
Advanced hydraulic modular valve block with compact structure and less tube circuit increasing the reliability and maintainability
Linked oil cylinders ensure consistent shearing angle during the shearing processing.
Accumulator keeps return stroke accurately and rapidly; and gap between blades can be adjusted in an accurate, rapid and convenient way by hand wheel.
Shearing angel is adjustable, which decreases the distortion of sheet; convenient and accurate back gauge position electric control and display.
Rolling material support balls decreases scratch of sheet and reduces frictional resistance.
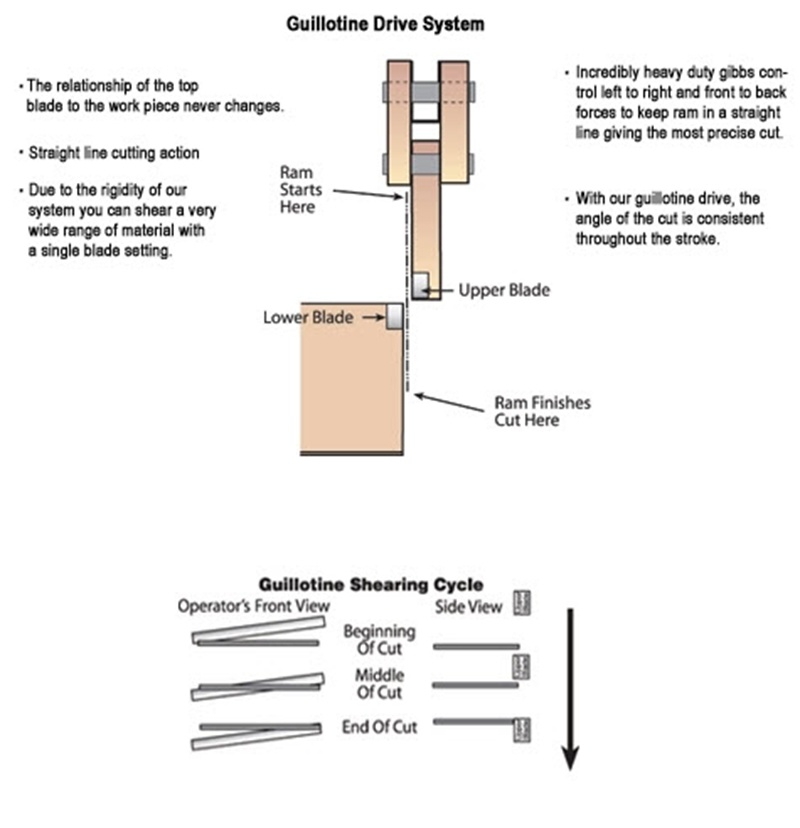
The machine used is called a squaring shear, power shear, or guillotine. The machine may be foot powered, less commonly hand powered, or mechanically or hydraulically powered. It works by first clamping the material with a ram. A moving blade then comes down across a fixed blade to shear the material.

Optional Numeric Control System
Nanjing Estun E21S E200PS
Back gauge controlling; General motors control; Intelligent positioning;;
Two programmable digital output; Work piece counting
40 program memory 25 steps for each program; Unilateral positioning; Concession function
One key to parameter backup and recovery; Metric system; Chinese/English.
DAC310
Holland Delem
1. Servo control technology;
2. Bright LCD display, 128 x 64 pixels;
3. Blades gaps controlling;
4. Cutting length limiting;
5. Back gauge actual and programmed position Displaying.
DAC360
Holland Delem
I .The panel control, high brightness LCD screen;
2. Controlling moving and concession of backgauge;
3. Setting cutting angles and gaps;
4. Managing shearing stroke and pressure;
5. Axis can do manual movement
For larger shears the moving blade may be set on an angle or "rocked" in order to shear the material progressively from one side to the other; this angle is referred to as the shear angle. Setting the blade on an angle decreases the amount of force required, but increases the stroke. A 5 degree shear angle decreases the force by about 20%. The amount of energy used is still the same. The moving blade may also be inclined 0.5 to 2.5°, called the rake angle, to keep the material from becoming wedged between the blades. However, raking the blade compromises the squareness of the edge.
The machine consists of a shear table, work-holding device, upper and lower blades, and a gauging device. The shear table is the part of the machinery that the workpiece rests on while being sheared. The work-holding device is used to hold the workpiece in place and keep it from moving or buckling while under stress. The upper and lower blades are the piece of machinery that actually do the cutting, while the gauging device is used to ensure that the workpiece is being cut where it is supposed to be.
-
Machine parts
Working table with ball roller
NC system
Ball screw + linear guide
Back gauge
Electronic system
Blade gap adjustment wheel
Frequency Inverter
Tube connector
Main motor
X-axis Motor
Hydraulic Valve
Oil pump
Machine optional parts
CNC control system
Blade gap adjustment motor
Light curtain in front side or back side
Air cooled
Front support + guide rail
Pneumatic rear support
-
Get a Free Quote
We will contact you within one working day. Please pay attention to your email.
To: Company Name
Related Products










